Glass Fiber Reinforced PP (PP GF), also known as glass fiber polypropylene or glass-filled PP, has become a cornerstone material in modern engineering and manufacturing. Its lightweight properties, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced mechanical performance make it indispensable for industries such as automotive, construction, and consumer goods. By offering a perfect balance of strength, rigidity, and affordability, glass fiber reinforced polypropylene are go-to solutions for diverse applications.

Understanding Glass Fiber Reinforced PP (PP GF): Composition and Grades
What is Glass Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Compound?
Glass fiber reinforced polypropylene (commonly referred to as GF PP or glass-filled polypropylene) is a composite material made by blending polypropylene with glass fibers, typically ranging from 10% GF to 60% GF. Grades such as PP GF10, PP GF15, PP GF20, PP GF25, PP GF30, and PP GF50 are tailored to specific performance needs, offering manufacturers flexibility.
PP GF30 materials, for instance, are one of the most popular grades and widely used due to their superior balance of strength and cost-efficiency, making them ideal for structural and load-bearing applications.
Curious how PP GF Compound ranks for metal replacement? Find out here: Top Plastics for Metal Replacement.
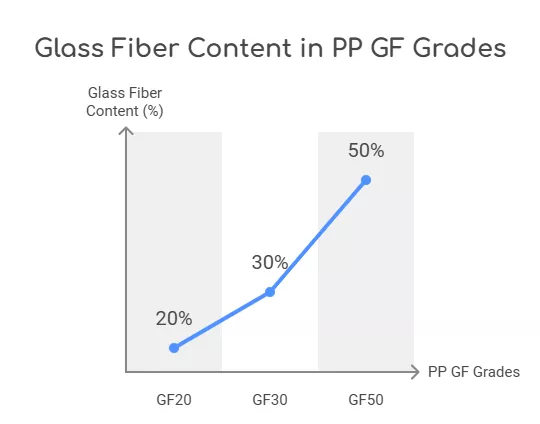
Characteristics of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Compound
The inclusion of glass fibers brings several key benefits to polypropylene:
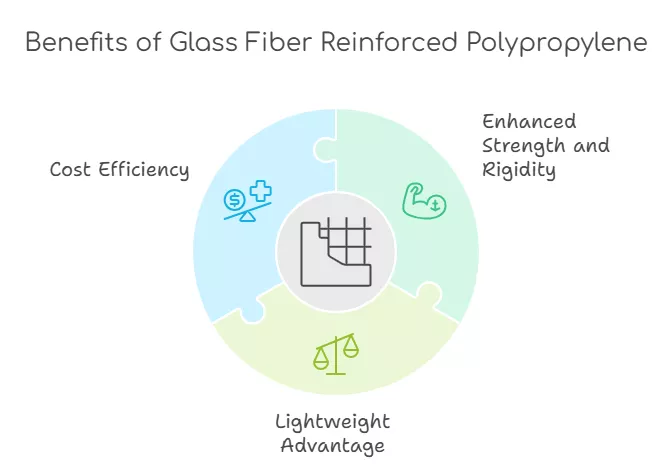
1. Enhanced Strength and Rigidity
Glass fibers boost tensile and flexural strength, making PP GF compounds suitable for load-bearing applications.
2. Lightweight Advantage
Compared to metals or other dense materials, PP GF offers a lightweight alternative while maintaining structural integrity.
3. Cost Efficiency
Combining the affordability of polypropylene with the performance of glass fibers creates a cost-effective solution for demanding applications.
Common Applications of Glass Fiber Reinforced PP
PP glass fiber compounds are versatile and find applications in a range of industries, including:

Automotive: Components like interior trim, buttons, and certain under-the-hood parts benefit from PP GF materials.
Construction: Durable panels and glass fiber reinforced polypropylene piping are key structural elements.
Consumer Goods: Lightweight and cost-effective parts in sports equipment, furniture and common seen appliances.
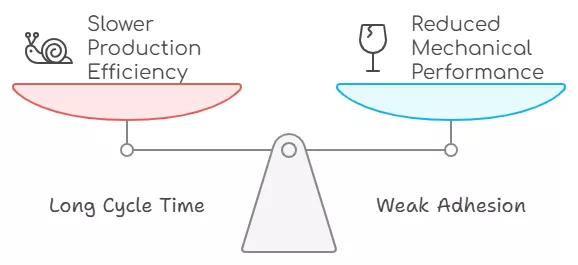
Challenges of Glass Fiber Reinforced PP
Despite their advantages, PP GF materials face two key challenges:
- Long Cycle Time in Injection Molding
PP GF materials often require longer injection molding cycles than other engineering plastics, which can slow production efficiency and increase costs. - Weak Adhesion Between PP and Glass Fibers
Due to the inherent incompatibility between the non-polar polypropylene matrix and polar glass fibers, weak adhesion can lead to reduced mechanical performance and fiber-floating issues.
Solutions to the Challenges of Glass Fiber Reinforced PP
- Optimizing Injection Molding
To address the challenge of extended cycle times in injection molding, optimizing the processing conditions is key. This includes fine-tuning mold temperatures, injection pressures, and cooling times. Additionally, innovative material formulations, such as flow enhancers or improved grades of PP GF, can help reduce cycle times and improve production efficiency without compromising material properties. - Strengthen Adhesion Between PP and Glass Fibers
A proven solution to weak adhesion is the use of maleic anhydride grafted polypropylene (MAgPP). Acting as a coupling agent, MAgPP chemically bonds PP with glass fibers, creating a stable polymer-fiber interface that improves mechanical properties and prevents fiber-floating issues..

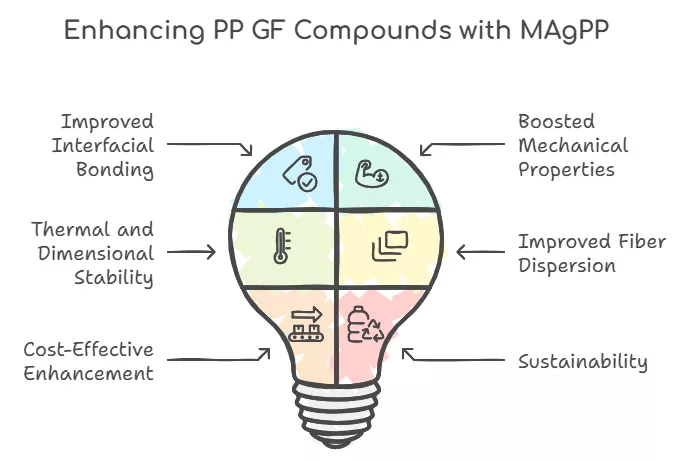
The Role of MAgPP in Addressing Adhesion Challenges
The integration of MAgPP into PP GF composites delivers several key benefits:
- Improved Interfacial Bonding: MAgPP enhances the strength and stability of the polymer-fiber interphase, allowing the glass fibers to act as an effective reinforcement.
- Boosted Mechanical Properties: With stronger adhesion, the composite exhibits higher tensile and impact strength, making PP GF composites suitable for demanding applications.
- Thermal and Dimensional Stability: MAgPP improves the thermal resistance and dimensional consistency of PP GF compounds, ensuring reliable performance even in extreme conditions.
- Improved Fiber Dispersion: MAgPP minimizes fiber floating by promoting better dispersion of glass fibers within the polypropylene matrix. This creates a more uniform material structure, resulting in smoother surface finishes and enhanced mechanical properties.
- Cost-Effective Enhancement: MAgPP maximizes the potential of cost-efficient glass fibers while minimizing the discard rate of defective products caused by floating fibers. This practical solution improves production efficiency and reduces material waste.
- Sustainability: MAgPP maintains the recyclability of polypropylene composites, ensuring that the addition of the coupling agent does not compromise the material's suitability for recycling processes. This supports eco-friendly manufacturing practices and promotes circular economy goals.
With its ability to address the adhesion challenge, MAgPP has become a critical enabler for manufacturers seeking to optimize the performance of PP GF materials. This advancement ensures that PP glass fiber compounds continue to evolve and meet the demands of modern engineering and manufacturing.
Mechanical Property Comparison
| Properties | PP raw material | PP GF30 | PP GF30 Enhanced with 20% MAgPP |
| Tensile Strength (Mpa) | 30 | 80 | 100 |
| Flexural Strength (Mpa) | 35 | 110 | 130 |
| Impact Strength (Kj/m2) | 3 | 8 | 13 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 0.9 | 1.12 | 1.13 |
Case Study: Enhancing PP GF for a Chair Manufacture
The Challenge: Weak Properties & Fiber-Floating Issue
A leading chair manufacturer faced a critical challenge with their PP glass fiber (GF) materials. Despite using GF reinforcement to improve the strength of their chairs, the final products exhibited weak tensile strength, leading to concerns about durability and long-term performance. Additionally, the chairs suffered from a fiber-floating issue, resulting in surface inconsistencies that impacted the visual and structural quality of the finished product.
The Solution: Introducing ENP – Our MAgPP Product
We recommended dry-blending 20% ENP to PP GF compound materials before injection molding, our proprietary maleic anhydride grafted polypropylene (MAgPP) solution, into the manufacturer's PP GF material formulation. Acting as a compatibilizer and coupling agent, ENP significantly improved the polymer-fiber interfacial bonding, transforming the material's performance without altering the manufacturing process.
The Result: Tangible Improvements
20% Higher Tensile Strength
Chairs became more durable and capable of withstanding long-term use.
30% Waste Reduction
The discard rate of defective products decreased significantly.
50% IncreasedProduction Efficiency
The discard rate of defective products decreased significantly.
100% Smooth Surface Finish
Fiber-floating issues were resolved, ensuring aesthetic and structural consistency.
Conclusion: A Comprehensive Win-Win Solution
With the integration of ENP, the chair manufacturer resolved their challenges, improving both the quality and sustainability of their products. The results included enhanced tensile strength, smoother finishes, reduced waste, and increased efficiency, demonstrating the transformative impact of MAgPP solutions on PP GF materials.

Ready to Enhance Your PP Glass Fiber Compounds?
Ready to take your glass fiber reinforced PP to the next level? Our maleic anhydride grafted polypropylene (MAgPP) solutions are designed to address the critical adhesion challenges and unlock the full potential of your materials. Whether you’re aiming to improve bonding between glass fiber and PP, eliminate fiber-floating issues, boost tensile strength, or achieve cost-effective and sustainable production, our products are designed to meet your specific needs. Check out the mechanical properties of ENP here.
Contact us today to learn how our MAgPP products can transform your PP GF composites, boosting their performance by up to 50% in efficiency. Let’s collaborate to create stronger, more reliable, and eco-friendly solutions tailored to your applications.

